B09 - Immune-related cell death pathways as targets of fungal virulence strategies

Isabel Saur
University of Cologne, Institute for Plant Sciences
Contact: isabel.saur(at)uni-koeln.de
For more information visit: Saur Lab
Abstract
This project is funded within the 2nd funding period of the SFB 1403, starting from 2024
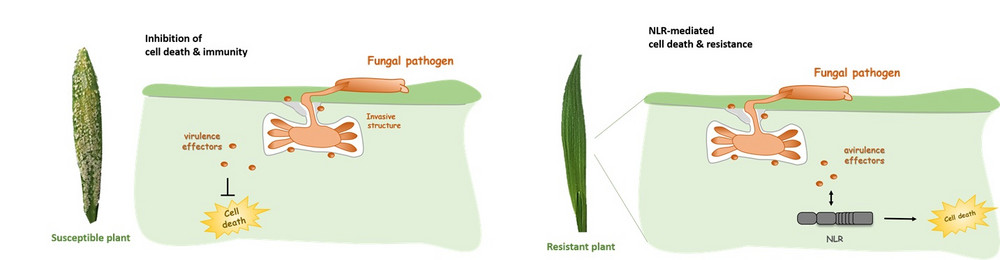
Obligate biotrophic phytopathogens such as the barley powdery mildew fungus Blumeria hordei require living host cells for proliferation and the establishment of disease symptoms. Thus, the maintenance of intact living host cells and inhibition of host cell death by pathogen virulence effectors is of utmost importance for biotrophs. In turn, NLR-mediated cell death mediates pathogen resistance by detecting pathogen avirulence effectors. In this project we investigate cell death signalling in cereals and determine host cell death components targeted by pathogen effectors. We also develop strategies to translocate pathogen effectors to the host cells and thereby rely on NLR-mediated cell death as a read out for successful effector translocation to the host cells.
Recent Publications
Lawson AW, Flores-Ibarra A, Cao Y, An C, Neumann U, Gunkel M, Saur IML, Chai J, Behrmann E, Schulze-Lefert P. The barley MLA13-AVRA13 heterodimer reveals principles for immunoreceptor recognition of RNase-like powdery mildew effectors. EMBO J. 2025 Feb 13. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00373-9. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39948409.